Navigating the maze of CPT and diagnosis codes for medical procedures can be a daunting task, not just for healthcare providers but also for medical coders, billers, and even patients.
Bronchoscopies are a case in point—what seems like a straightforward procedure is actually classified under a variety of codes depending on its complexity, equipment used, and purpose. This blog post aims to unravel the complexities behind coding for bronchoscopies.
The Basics

A bronchoscopy is a medical procedure that allows a doctor to examine the inside of the lungs, including the bronchi, which are the main pathways into the lungs. This is often necessary for diagnosing lung diseases, infections, or tumors.
Why is it Done?
Bronchoscopies are essential in various scenarios, such as assessing blockages, collecting tissue samples, or even treating conditions directly by removing foreign bodies or excess tissue. Knowing how to code these procedures accurately is crucial for appropriate billing and reimbursement.
What are CPT Codes?
CPT stands for Current Procedural Terminology, a medical code set maintained by the American Medical Association. It’s widely used in the United States for coding outpatient and inpatient medical procedures.
Why Are They Important?
They are essential for standardized communication between healthcare providers and payers. They serve as a shorthand that summarizes the type, location, and complexity of each procedure, helping in accurate billing and medical records.
Essential CPT Codes for Bronchoscopies
Basic Bronchoscopy Codes
- 31622: Diagnostic bronchoscopy
- 31623: Bronchoscopy with brushings
- 31624: Bronchoscopy with lavage
The above codes are among the most frequently used for basic bronchoscopies. They are categorized based on what is done during the procedure.
Specialized Bronchoscopy Procedures
- 31625: Bronchoscopy with biopsy
- 31628: Bronchoscopy with transbronchial lung biopsy
- 31629: Bronchoscopy with transbronchial needle aspiration
These codes are used for more specialized bronchoscopies where specific interventions like biopsies or aspirations are performed. Accurate use of these codes is vital for proper billing and insurance claims.
Diagnosis Codes Explained
The Role of ICD-10
Diagnosis codes are standardized codes used to identify and classify diseases and conditions. The most commonly used system in the United States is the ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Edition).
Bronchoscopy-Related Diagnosis Codes
Common ICD-10 codes relevant to bronchoscopies include:
- J98.11: Atelectasis
- J45.909: Unspecified asthma
- C34.90: Malignant neoplasm of unspecified part of unspecified bronchus or lung
These diagnosis codes are crucial in indicating the medical necessity of the bronchoscopy, affecting insurance coverage and reimbursement rates.
How to Accurately Code for Bronchoscopies
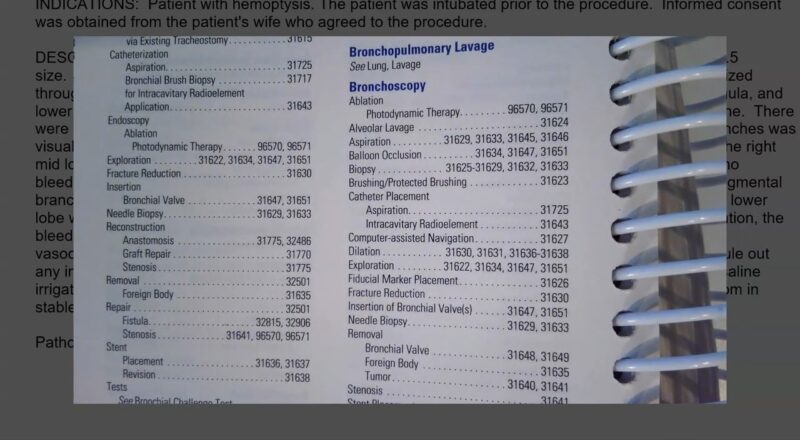
When coding for bronchoscopies, it’s not just about the procedure code; often, additional codes like anesthesia codes, modifier codes, or even equipment codes might be necessary.
- Anesthesia Codes: Like 00520 for anesthesia during bronchoscopy
- Modifier Codes: Such as 22 for increased procedural services
- Equipment Codes: E.g., A4616 for endotracheal tube
Documentation is Key
Accurate documentation is a linchpin in correct coding. Everything from patient history to the details of the procedure, like equipment used or any complications, needs to be meticulously recorded. The more detailed the documentation, the easier it will be to select the most accurate codes.
Common Errors and How to Avoid Them

- Upcoding: This is coding for a more complex procedure than was actually performed. This could result in penalties.
- Undercoding: This means coding for a less complex procedure, which could lead to a loss of revenue.
- Incorrect Diagnosis Codes: Coding a diagnosis that does not justify the medical necessity for a bronchoscopy can result in claim denials.
Best Practices
- Ongoing Education: Both clinicians and coders should engage in regular training sessions to stay updated on the latest coding guidelines.
- Double-Checking: Before submitting, double-check the codes against the medical records to ensure accuracy.
- Audit Trails: Maintain a thorough audit trail for every coded procedure as a safeguard against any queries or audits.
Importance of Accurate Coding for Quality of Care

Patient Safety and Quality Metrics
When it comes to healthcare, quality of care is paramount. Believe it or not, accurate coding goes beyond financials and directly impacts quality metrics. For example, codes provide data for outcomes research, which can influence medical guidelines and ultimately affect patient care.
Risk Adjustment and Population Health
Proper coding allows for effective risk adjustment in patient populations, ensuring fair reimbursement for providers treating sicker patients. This also enables better tracking of patient outcomes and can drive improvements in population health management strategies.
Bridging the Gap Between Clinicians and Coders

The Need for Collaboration
Medical coding is often seen as the responsibility of coders and billing specialists. However, a successful coding process is a collaborative effort that involves clinicians, coders, and sometimes even patients. Clinicians must understand what coders need to look for, and coders should have a basic understanding of medical procedures and diagnoses.
How to Foster Teamwork
- Regular Meetings: A quick monthly or quarterly meeting can go a long way in resolving any coding issues and providing updates.
- Feedback Loop: Create a system where coders can easily ask clinicians for clarification and vice versa.
- Documentation Training: Consider conducting joint training sessions where clinicians and coders can learn the nuances of effective clinical documentation and coding.
The Financial Impact of Coding Errors

Lost Revenue and Legal Risks
Coding errors can have significant financial repercussions. Upcoding can result in severe legal consequences, while undercoding could mean a loss of revenue for healthcare providers. Additionally, frequent errors can trigger audits, which can be costly in terms of time and resources.
The Cost of Claim Denials
Claim denials due to incorrect coding can be a hidden drain on a healthcare institution’s finances. According to industry statistics:
- Claim denial rates can range between 5-10%.
- It costs around $25 to rework a denied claim.
- About 65% of denied claims are never resubmitted.
The above figures underline the critical importance of getting coding right the first time around.
Coding Software and Automation

Automation and software solutions are increasingly playing a significant role in medical coding. Software programs can auto-generate codes based on electronic medical records, significantly reducing the risk of human error.
- Faster coding processes
- Reduced manpower costs
- Improved accuracy
- Software limitations in understanding complex medical scenarios
- Dependence on initial input quality (Garbage In, Garbage Out)
While software can offer significant benefits, the human element in medical coding cannot be entirely replaced. Medical coders still need to oversee the automated process for best results.
FAQs
What should be done if multiple procedures are performed during a single bronchoscopy session?
If multiple procedures are performed during a single bronchoscopy session, each procedure typically requires its own CPT code. However, you may also need to use modifier codes to indicate that multiple procedures were performed during the same session. These modifier codes help ensure that each procedure is billed appropriately and avoids double billing for the same service component.
How often are CPT codes for bronchoscopies updated?
The American Medical Association (AMA) typically releases updates to the CPT code set annually, usually effective from January 1st of the new year. However, mid-year updates can also occur if there are significant changes or new procedures introduced. It’s crucial to keep an eye on updates from the AMA to ensure coding accuracy.
Are there specific CPT codes for pediatric bronchoscopies?
While the core CPT codes for bronchoscopies apply across age groups, pediatric bronchoscopies cases may sometimes require additional modifier codes to indicate the age of the patient or the complexity due to the patient’s age. Always consult the latest CPT coding guidelines to ensure you’re coding pediatric cases accurately.
How do CPT codes for bronchoscopies differ from E/M codes?
CPTs for bronchoscopies are procedure-specific and are used to specify exactly what kind of bronchoscopy was performed. E/M codes, or Evaluation and Management codes, are used to describe the complexity of care for patient visits and are typically used for office visits, consultations, and other non-procedural services.
While E/M codes may accompany a bronchoscopy procedure to describe patient evaluation, they are separate from the actual bronchoscopy CPT codes.
What do you do if a code is rejected by an insurance company?

If it is rejected, the first step is to review the claim and the coding to ensure there were no errors in the initial submission. If the coding was accurate, it might be necessary to appeal the decision, providing additional documentation or clarification to support the medical necessity of the bronchoscopy.
The appeal process can vary between insurance providers, so consult your payer’s guidelines for detailed steps.
Can bronchoscopy codes be used for telehealth services?
Generally, bronchoscopy codes are meant for in-person procedures and are not applicable to telehealth services since a bronchoscopy cannot be performed remotely. However, the consultation or discussion related to a bronchoscopy procedure could potentially be coded for telehealth using the appropriate E/M codes and telehealth modifiers.
Concluding Thoughts
Understanding CPT and diagnosis codes for bronchoscopies may appear challenging at first, but with a systematic approach and a deep dive into the coding world, it becomes manageable. Accurate coding ensures proper billing and fortifies the healthcare system’s financial sustainability.
Quick Tips for Success
- Always rely on detailed and thorough documentation.
- Continually update your knowledge base, whether you’re a healthcare provider or a medical coder.
- Establish checks and balances within your coding system to catch and rectify errors before claims are submitted.
Knowing about the nuances of coding is not just for the healthcare providers and coders; it’s for anyone invested in the healthcare ecosystem. It helps in demystifying the medical bills and makes healthcare a more transparent industry. So, the next time you come across a bronchoscopy, whether in a medical report or a bill, you’ll know exactly what those codes mean!

